What Is an SNI Bug Host? Full Beginner Guide
If you’re new to VPN tunneling, free internet configurations, or apps like HA Tunnel, HTTP Injector, Stark VPN, and others, you’ve probably come across the term SNI Bug Host. It might sound complicated at first, but don’t worry this guide breaks everything down in a simple, beginner-friendly way.
Whether you want to create your own VPN files, understand how free-internet tricks work, or explore network security concepts, this full SNI Bug Host guide will help you understand everything step-by-step.
1. What Is an SNI Bug Host?
An SNI Bug Host is a domain name used inside a VPN app to bypass network restrictions. SNI stands for Server Name Indication, a feature used in HTTPS connections that tells the server which website you want to access.
Normally, your ISP (internet provider) expects this SNI to match the website you’re visiting. But when a domain has a misconfiguration, open access, or free routing, it becomes a bug host meaning it can be used to access the internet without using normal mobile data bundles.
👉 In simple terms: An SNI Bug Host is a website domain that allows a VPN to connect even when you don’t have data.
2. How Does an SNI Bug Host Work?
To understand this, think of SNI as the “website name” inside an encrypted TLS/SSL connection.
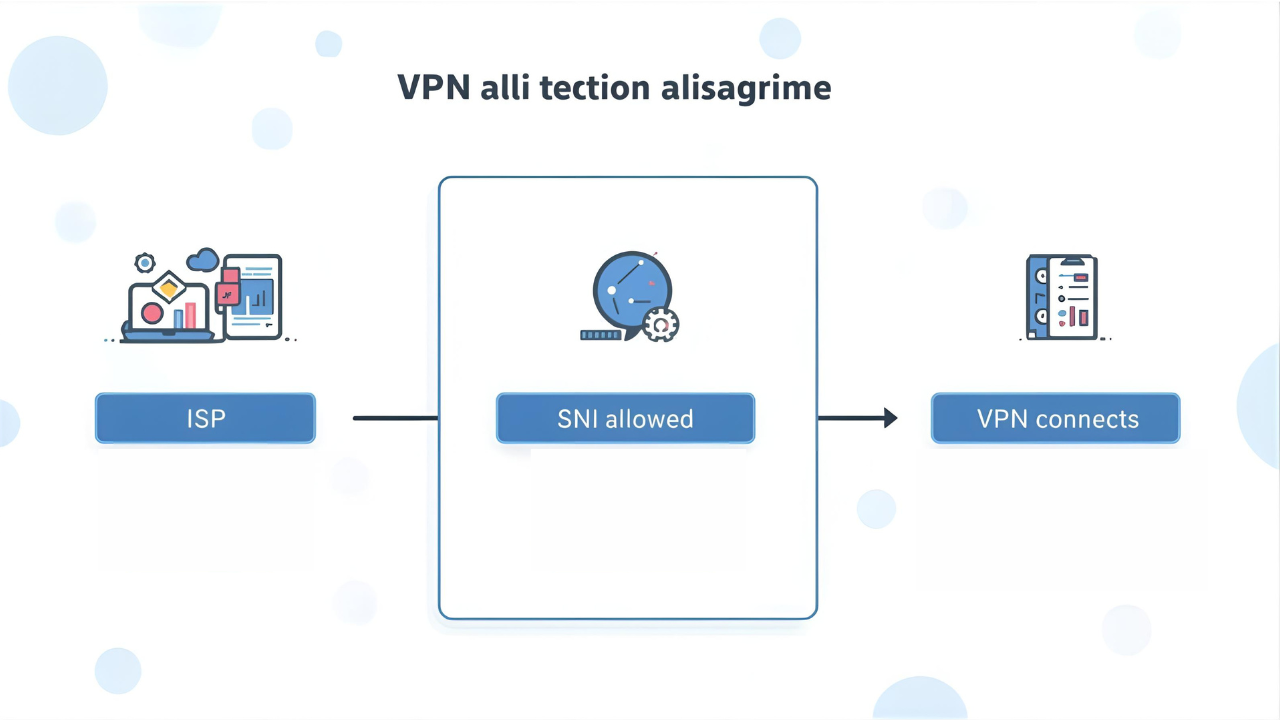
When you try to browse the internet:
- Your phone sends the SNI request to the ISP.
- The ISP checks if you have data or not.
- If the SNI host has special access (like a zero-rated domain), it is allowed through.
- A VPN tunnels through this domain and gives you full internet access.
A zero-rated domain means the ISP allows the site to load even if you don’t have data. Examples include:
- Educational sites
- Government portals
- Social media promo sites
- Network self-service portals
When their SNI is used inside a VPN app, the VPN can sneak through, creating a working connection.
3. Why Do People Use SNI Bug Hosts?
1. Free Internet Tunneling
This is the most common reason. A working SNI can allow tunneling apps to connect for free.
2. Creating VPN Config Files
Creators use SNI hosts to build HA Tunnel files, HTTP Injector configs, KPN Tunnel files, Dark Tunnel or TLS Tunnel configs.
3. To Bypass Restrictions
Some ISPs restrict normal traffic but allow certain domains. Using the SNI trick lets users access blocked services.
4. Network Testing
Developers use SNI hosts to test whether their domains are zero-rated or misconfigured.
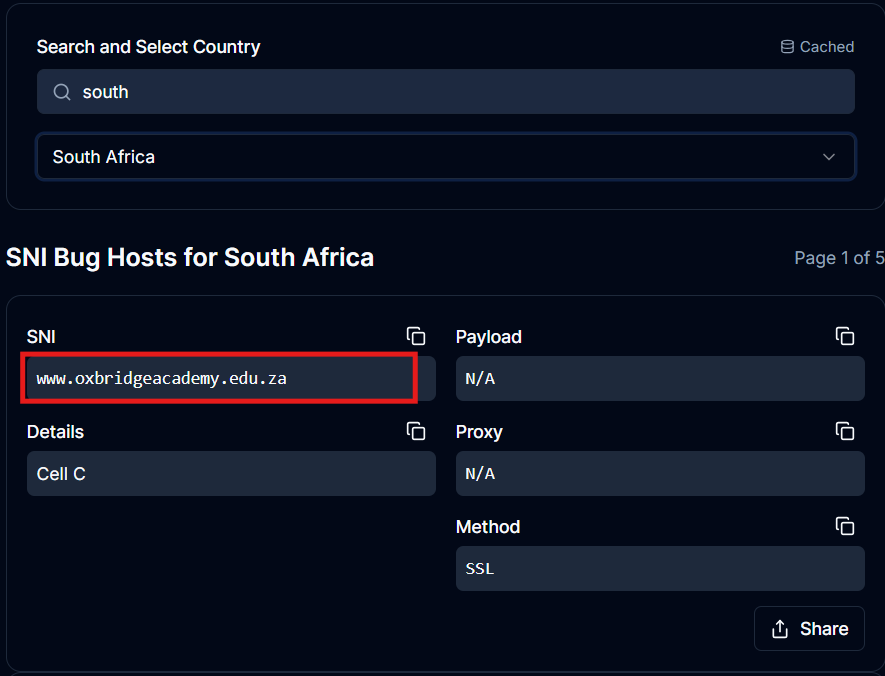
4. Examples of SNI Bug Hosts
These are not guaranteed to work, but they show what real bug hosts look like:
- Zero-rated educational sites (e.g., university portals)
- Self-care portals (cell network login pages)
- Promo sites like free Facebook mode domains
- Government public sites
- CDN or cloud service subdomains
A bug host usually looks like:
- example.mtn.co.za
- free.facebook.com
- zero-rated.website.gov
- cdn.portal.network.net
Working hosts differ by country and by ISP. Your network might block some while allowing others.
5. How to Find or Generate an SNI Bug Host
🔹 1. Check Zero-Rated Sites
Your ISP usually lists websites that work without data. These are your best candidates.
🔹 2. Scan Using Online Host Checkers
Tools can check if a domain responds without data. Our website has a generator that helps users get hosts by country.
Open SNI Generator🔹 3. Test Using VPN Apps
Apps like HTTP Injector, TLS Tunnel, and HA Tunnel allow you to test if a specific SNI creates a successful handshake.
6. Common Apps That Use SNI Bug Hosts
These tunneling apps rely heavily on SNI hosts:
All these apps let users input SNI, Payload, Proxy, and Custom headers. The SNI is often the most important part.
7. Risks of Using SNI Bug Hosts
While SNI hosts are widely used, you should know the risks:
- Connection might stop working anytime: If the ISP fixes the bug, the host becomes useless.
- Some bug hosts may be unstable or slow
- Using random hosts from Telegram groups is risky: Some hosts may redirect to harmful sites.
- Not allowed in some regions: Always check local rules before using tunneling tricks.
🎯 Final Thoughts
An SNI Bug Host is simply a website domain that a mobile network allows for free, which can then be used by tunneling apps to create working internet connections. They are extremely popular because they’re easy to use and help users connect when they have no data.
If you’re a beginner, this guide gives you everything you need to understand what an SNI is, how bug hosts work, how to find them, and why VPN apps use them.